What is a Domain Reseller?
26.01.2026
Seize the Opportunity: $3 Rebate on ccTLD-Matched .COM Registrations
30.01.2026Are you curious about service oriented architecture? In this article, we will provide answers to several questions, including ‘What is an SOA,’ its functions, and its benefits.
What is SOA?
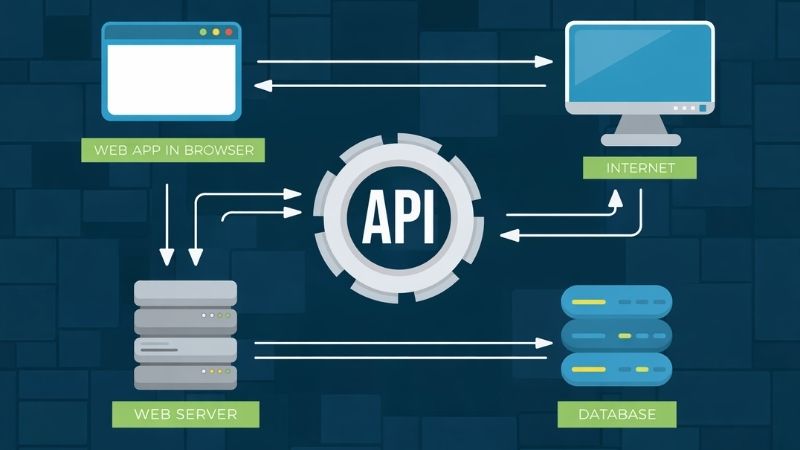
Are you wondering what is an SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture)? SOA is one of the best ways to design software systems. In this architecture, every service works separately and independently. These independent services connect with each other via APIs.
The main purpose of service oriented architecture is to create flexible, manageable, and simple software services. Each service does one specific thing. For example; user management, payments, billing, or reporting services all work separately. If you need to perform maintenance or fix a bug, other services will not be affected.
SOA is a great choice, especially for large and complex systems. For example, what is software oriented architecture often used for? It is mostly used in:
- Domain Reseller Programs (such as domain registration and management platforms powered by APIs like domainnameapi.com)
- Banking
- E-Commerce
- SaaS Projects
Another key advantage of SOA is scalability. If one service receives high traffic, you can easily upgrade only that specific service. Furthermore, if any issue occurs, it does not affect your entire project.
How Does SOA Work?
SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture) is a software system where different services work independently. Each service has its own task. Because they are independent, if one service has a problem, the others are not affected and continue to work properly. All services connect to each other using APIs.
Example:
- User Management Service
- Payment Service
- Billing Service
These three services work separately. If one service fails, the others keep working normally and remain unaffected.
Key Principles of SOA
Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) is not just about separating services; it is about organizing them for specific rules and purposes.
- Loose Coupling: Services work independently. This means changing one service does not break the other services.
- Reusability: Services are built to be used for multiple different projects.
- Service Contracts: Services follow strict rules.
This approach makes the system flexible, easy to maintain, and scalable.

SOA vs. Microservices
What is the difference with SOA and Microservices? SOA is an architecture used mostly in large enterprise systems, where services communicate with each other through a central structure (usually an ESB). Therefore, services are more comprehensive, and because there is a central management point, making changes and scaling is relatively slower. Microservices, on the other hand, is a modern approach where each service performs a single, small task, is developed independently, and can be deployed independently. Services communicate directly using lightweight protocols, making the system more flexible and faster. In short, while SOA prioritizes order and standardization, Microservices prioritizes speed, flexibility, and scalability.
Main Benefits of SOA
The main benefits of SOA are flexibility, reuse, and easy system integration. Applications are built as separate services, so you can add or update a service without affecting the whole system. The same service can be used by different applications, which saves time and reduces development costs. SOA also allows systems built with different technologies to communicate smoothly using common standards, making it a strong and sustainable choice for large organizations.

Challenges of SOA
The main challenges of SOA are complexity, management overhead, and performance concerns. Because SOA often relies on centralized components like an Enterprise Service Bus (ESB), the system can become difficult to design, manage, and maintain over time. As the number of services grows, governance, versioning, and coordination between teams require extra effort. In addition, the use of heavier communication protocols can increase latency, which may negatively affect performance if the architecture is not carefully planned.